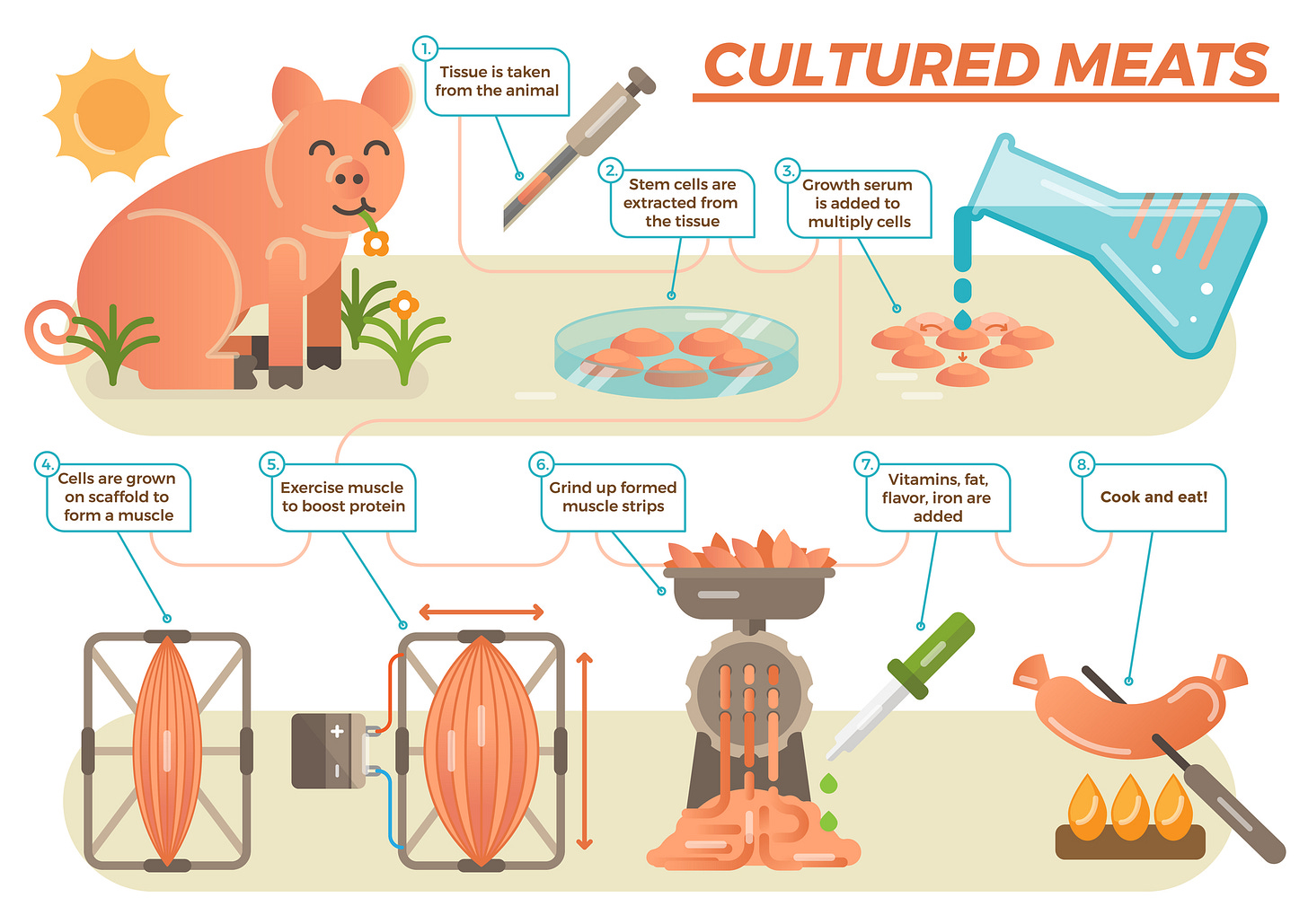
In the ever-evolving landscape of food technology, lab-grown meat has emerged as a potential solution to address the ethical and environmental concerns associated with traditional animal agriculture. However, from a vegan standpoint rooted in principles of compassion and sustainability, the ethical implications of lab-grown meat are far from clear-cut.
Negotiating the ethical complexities of lab-grown meat is a unique challenge for vegans. Despite its potential to reduce animal suffering, concerns about animal-derived components, environmental impact, and alignment with vegan values persist. Advocates for social justice and compassionate living must critically assess the implications while promoting sustainable plant-based alternatives.
This article looks into the complex considerations surrounding lab-grown meat and its potential dissonance with the core values of veganism.
Defining Veganism
Veganism, at its heart, is a lifestyle choice that seeks to exclude all forms of animal exploitation. This extends beyond food consumption to encompass clothing, entertainment, and any other use of animals for human purposes. Vegans are driven by a deep commitment to minimizing harm to all living beings and promoting ecological justice. Lab-grown meat, while seemingly eliminating the direct slaughter of animals, presents a unique ethical quandary to some, challenging the very foundation of vegan principles.
Ethical Concerns
Several key concerns regarding lab-grown meat resonate with the vegan ethos:
Animal-derived Components: Currently, many methods of cultivating meat still rely on fetal bovine serum, a growth factor extracted from pregnant cows. This contradicts the vegan commitment to avoiding any form of animal exploitation, even if it occurs at an earlier stage of life.
Environmental Impact: While lab-grown meat eliminates certain environmental burdens associated with conventional animal agriculture, such as land use and greenhouse gas emissions, its production process can be energy-intensive. The reliance on complex growth mediums and specialized facilities raises questions about the technology's overall sustainability and long-term environmental impact.
The Disconnect from Vegan Values
Veganism extends beyond mere abstention from animal products; it embodies a profound philosophy encouraging mindfulness and interconnectedness with all living beings. Delving into the nuances of this lifestyle, the advent of lab-grown meat introduces a paradigm shift by eliminating the direct link between consumption and animal harm. However, this innovative approach might unintentionally foster a disconnect from the broader ethical and environmental implications inherent in our food choices.
As lab-grown meat replaces the tangible awareness of animal suffering with a seemingly "clean" alternative, there lies a potential risk of diminishing the significance attached to building a more compassionate and sustainable food system. It prompts reflection on the intricate interplay between choices and consequences, urging a more comprehensive understanding of the multifaceted aspects of ethical living. Thus, as vegans navigate this evolving landscape, it becomes crucial to delve deeper into the potential implications of embracing lab-grown meat and consider how it may shape perceptions and values within the broader context of compassionate and sustainable living.
Advocating for Plant-Based Alternatives
In the contemplation of these ethical considerations, it is incumbent upon vegans to proactively prioritize the advocacy and increased accessibility of an extensive array of plant-based alternatives. The continuous strides in food science have yielded a diverse spectrum of not only delicious but also highly nutritious plant-based options. These choices not only align seamlessly with vegan principles but also contribute significantly to the overarching goal of forging a more sustainable and eco-conscious future.
As vegans focus their efforts on the promotion of these readily available and palatable solutions, they are effectively positioned to champion a food system characterized by compassion and environmental responsibility. In doing so, they steadfastly uphold their core values without any compromise, fostering a broader societal understanding and appreciation for a lifestyle that harmonizes ethics, health, and sustainability in the realm of nutrition.
Summary
Navigating the ethical complexities of lab-grown meat presents a unique challenge for vegans. While the technology may offer a potential reduction in animal suffering compared to traditional meat production, the ethical concerns surrounding animal-derived components, environmental impact, and the potential disconnect from vegan values cannot be ignored. As advocates for social justice and compassionate living, the vegan community must critically evaluate the implications of embracing lab-grown meat and continue championing plant-based alternatives as a more aligned and sustainable choice.
Sources:
General Resources
Books:
Dominion: The Power of Animals in Nature and in Our Imagination by Matthew Scully
Animal Liberation by Peter Singer
Eating Animals by Jonathan Safran Foer
A Billion Hungry Mouths: Feeding the World Without Consuming the Planet by Colin Tudge
Websites and organizations:
Documentaries:
Academic articles:
"The Case for Animal Rights" by Tom Regan
‘‘Why We Love Dogs, Eat Pigs, and Wear Cows: An Introduction to Carnism’’ by Melanie Joy
‘‘Animal Rights: The Abolitionist Approach’’ by Gary L. Francione
‘‘Fellow Creatures: Our Obligations to the Other Animals’’ by Christine Korsgaard
Receive a single informative article daily at 12:01 AM by email. For additional updates, explore my homepage with exciting vegan and plant-based news content and delightful and delicious recipes. Stay connected to the vegan world and all it has to offer.
Visit The Vegan Project Global our Facebook page for more vegan outreach and education.
Also, visit our new YouTube channel