For vegans seeking to optimize their nutrient intake, both blending and juicing offer unique advantages and drawbacks. Understanding these nuances can empower you to choose the preparation method that best aligns with your health goals and preferences.
This guide dives deep into the key differences between blending and juicing, exploring their impact on nutrient content, fiber intake, satiety, and overall health benefits. By weighing the pros and cons of each approach, you can make informed decisions about incorporating them into your vegan diet.
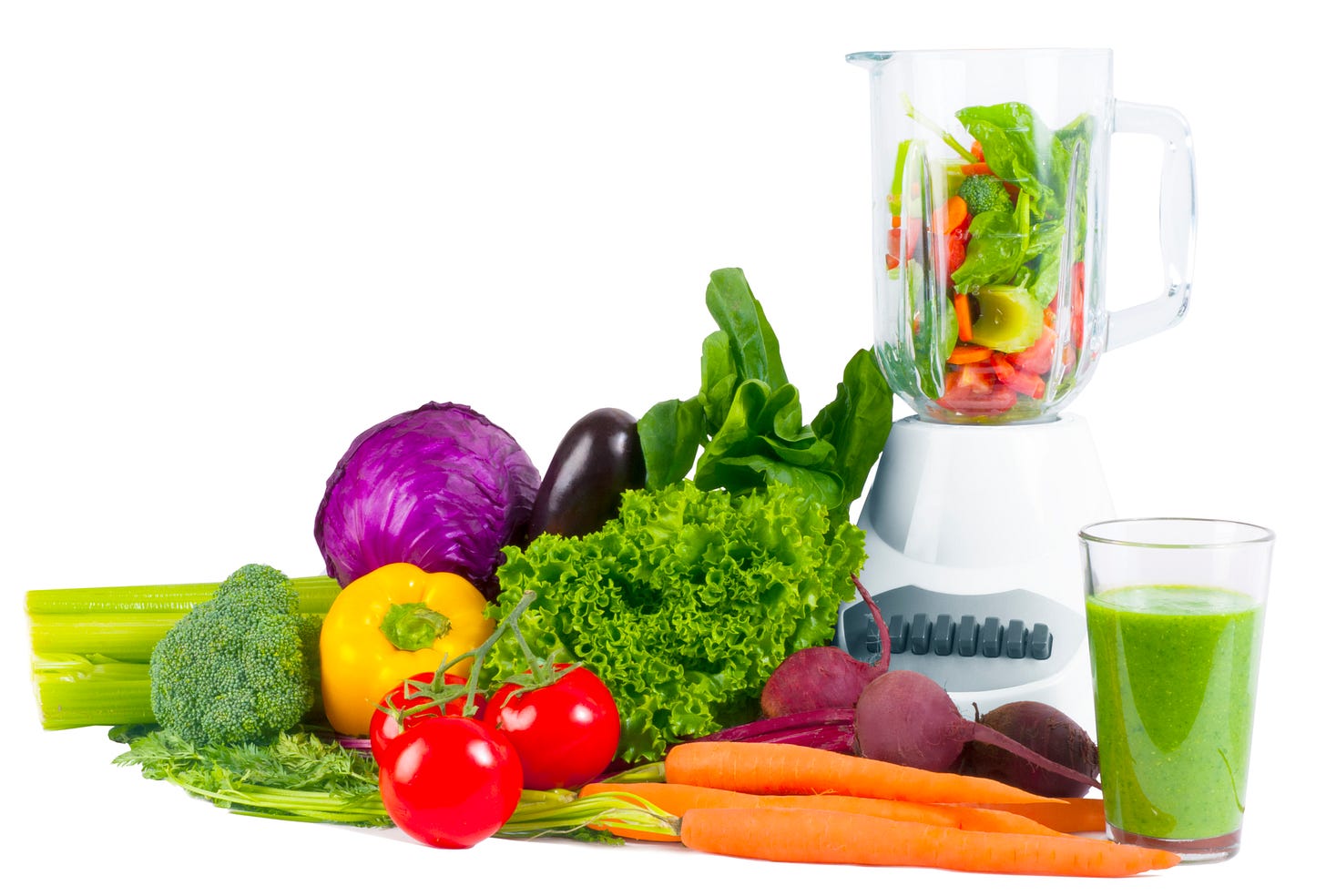
Blending:
Blending whole fruits and vegetables into smoothies retains all the fiber, vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds. This translates to several key advantages:
1. Fiber Powerhouse: Fiber is crucial for digestive health, gut microbiome balance, and promoting satiety. Blending preserves crucial fiber content, keeping you feeling fuller for longer and aiding in healthy digestion.
2. Nutrient Versatility: Smoothies offer a wider platform for incorporating diverse ingredients, including leafy greens, herbs, nuts, and even protein powder or healthy fats. This allows for tailoring your smoothie to address specific nutritional needs.
3. Lower Sugar Impact: Blending dilutes the natural sugars of fruits with fiber and water, mitigating potential blood sugar spikes compared to juicing.
4. Thicker and More Filling: The thicker consistency of smoothies can be more satisfying and promote satiety, leading to less snacking between meals.
However, blending also has some limitations:
1. Less Concentrated Nutrients: Compared to juices, blends offer a less concentrated dose of specific nutrients, as some may be lost during the blending process.
2. Digestion Considerations: The thicker consistency of smoothies might be challenging for individuals with digestive issues.
3. Potential for Calorie Overload: Depending on the ingredients used, smoothies can be higher in calories and sugar than juices.
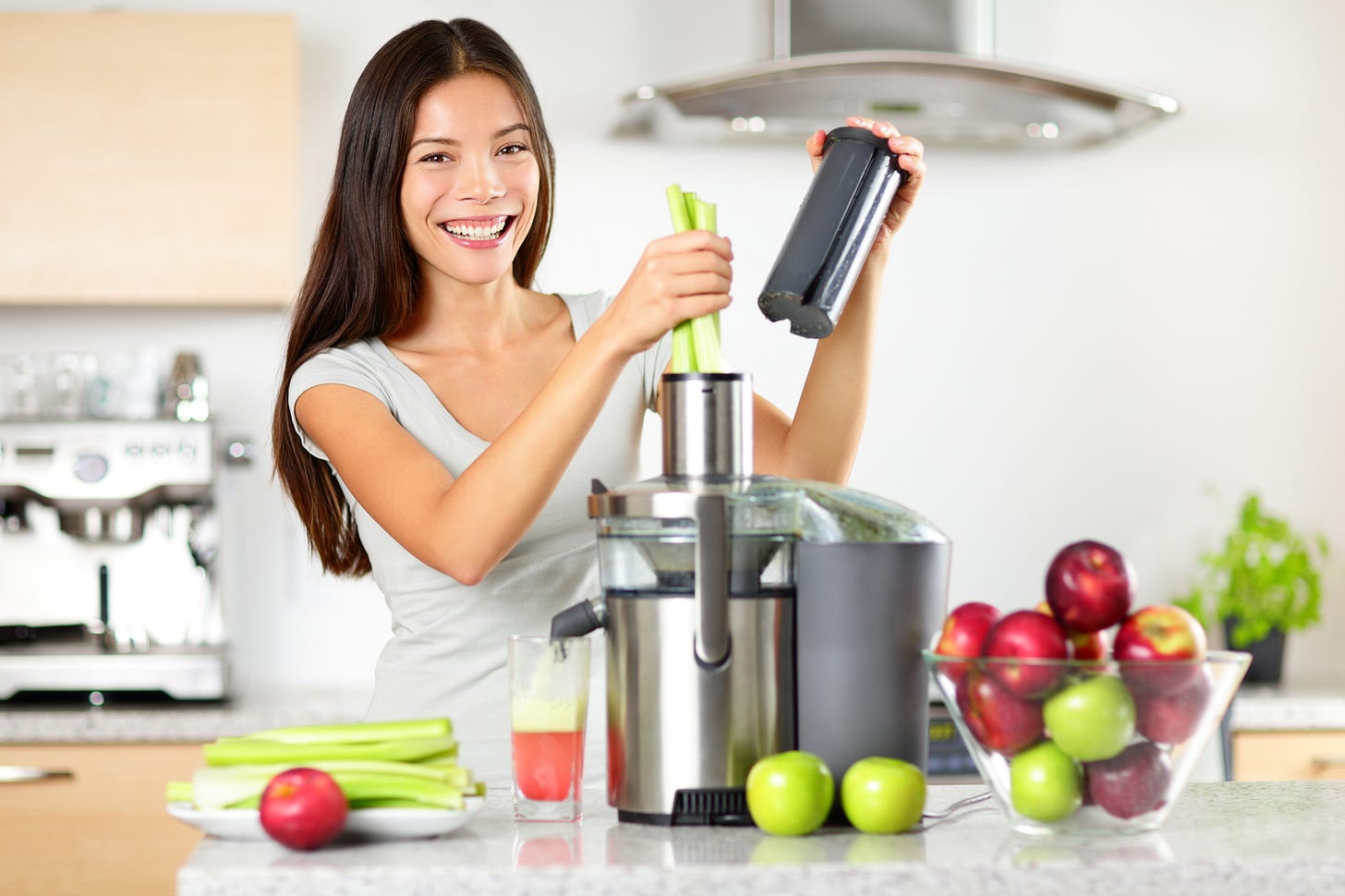
Juicing:
Juicing extracts the juice from fruits and vegetables, separating the liquid from the pulp and fiber. This process delivers a concentrated dose of nutrients, offering several benefits:
1. Nutrient Boost: Juices provide a concentrated hit of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which can be beneficial for those seeking to increase their intake.
2. Easier Digestion: The liquid form of juices allows for easier digestion, making them suitable for individuals with digestive sensitivities.
3. Quick and Convenient: Juicing offers a quick and efficient way to consume valuable nutrients, particularly when time is limited.
4. Detoxifying Potential: Juicing can be incorporated into detox programs, promoting the elimination of toxins and supporting liver health.
However, juicing comes with its own set of drawbacks:
1. Loss of Fiber: The juicing process removes all the fiber from fruits and vegetables, which can lead to digestive issues, constipation, and decreased satiety.
2. High Sugar Content: Juices made with sugary fruits like oranges, grapes, and mangoes can be significantly higher in sugar than whole fruits.
3. Less Filling: The absence of fiber in juices contributes to lower satiety compared to smoothies, leading to increased hunger pangs.
4. Nutrient Degradation: Certain nutrients, such as vitamin C, can be degraded during the juicing process, potentially impacting overall nutritional value.
5. Higher Calorie Content: Similar to smoothies, depending on the chosen ingredients, juices can be higher in calories than whole fruits and vegetables.
The Bottom Line:
Both blending and juicing offer unique benefits and drawbacks for vegans. Choosing the optimal method depends on your individual health goals and preferences. If you prioritize fiber intake and satiety, blending is the clear winner. However, if you seek a quick and convenient way to boost your nutrient intake, juicing can be a valuable tool. Remember to balance your approach and consume both whole fruits and vegetables alongside your chosen preparation method for optimal health.
Additional Resources:
Disclaimer: This guide provides general information and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult with your healthcare provider or registered dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
For more great vegan recipes plus great plant-based cooking tips and tricks join our popular Facebook group The Vegan Kitchen: Recipes + More!